
Understanding the components of a sewing machine is essential for effective operation and troubleshooting. Key parts include the spool pin, bobbin, and presser foot, each playing a vital role in stitch formation and fabric handling. While models vary, core elements remain consistent, ensuring a solid foundation for mastering sewing techniques.
1.1 Overview of Sewing Machine Components
Understanding the components of a sewing machine is fundamental to mastering its operation. The machine consists of several key elements, each designed to perform specific tasks. The spool pin holds the thread, while the bobbin and bobbin case manage the bottom thread, ensuring proper tension. The take-up lever adjusts thread tightness, and the presser foot controls fabric movement. Other essential parts include the feed dog, which moves fabric, and the needle, which creates stitches. While modern machines may vary in features, the core components remain consistent, enabling users to sew efficiently. Familiarizing oneself with these parts is the first step in unlocking the machine’s full potential for creative sewing projects.
1.2 Importance of Understanding Sewing Machine Parts
Understanding the parts of a sewing machine is crucial for optimal performance and troubleshooting. Knowing each component’s function allows users to thread the machine correctly, adjust tensions, and resolve common issues like uneven stitches or thread breakage. Proper comprehension also enhances safety, as incorrect usage can lead to accidents. Additionally, familiarizing oneself with the machine’s components enables better maintenance, extending its lifespan. Whether for personal projects or professional sewing, a solid grasp of the machine’s anatomy is indispensable for achieving desired results efficiently and effectively.


Basic Parts of a Sewing Machine
The essential components of a sewing machine include the spool pin, bobbin, take-up lever, thread guide, and presser foot. These parts work together to ensure smooth stitching and fabric control, making them fundamental for effective sewing operations.
2.1 Spool Pin: Function and Purpose

The spool pin is a essential component located on the top of the sewing machine, designed to hold the spool of thread in place. Its primary function is to stabilize the thread supply, ensuring it feeds smoothly into the machine. Proper alignment and placement of the thread on the spool pin are crucial for maintaining consistent thread tension. The spool pin works in conjunction with the take-up lever and thread guide to direct the thread flow accurately. Understanding its role is vital for effective threading and operation, as incorrect placement can lead to threading issues and uneven stitching. Regular maintenance ensures the spool pin remains free from debris, promoting optimal performance.

2.2 Bobbin: Role in Stitch Formation
The bobbin is a small, cylindrical component that holds the bottom thread, playing a critical role in forming the underside of stitches. It works in tandem with the top thread to create interlocking loops, ensuring secure and even stitching. Properly winding and inserting the bobbin into the bobbin case is essential for consistent stitch formation. The bobbin’s thread tension must be balanced with the top thread to achieve optimal results. Incorrect bobbin threading or uneven winding can lead to poor stitch quality or machine malfunction. Regularly checking and maintaining the bobbin ensures smooth operation and professional-grade stitching in various sewing projects.
2.3 Bobbin Case: Tension and Thread Control
The bobbin case is a crucial component that houses the bobbin and regulates thread tension, ensuring smooth stitch formation. It works in conjunction with the bobbin to create the necessary thread loop for sewing. The case features a specific threading pattern that maintains optimal tension, preventing issues like loose stitches or thread breakage. Proper installation of the bobbin into the case is essential, as incorrect placement can disrupt tension control. The bobbin case also interacts with the take-up lever and presser foot to manage thread flow and fabric movement. Adjusting the bobbin case tension correctly ensures consistent stitching and prevents common sewing problems, making it a vital part of the machine’s functionality. Regular maintenance of the bobbin case is recommended for seamless operation.
2.4 Take-Up Lever: Thread Tension Adjustment
The take-up lever is a metal hook attached to the thread guide, responsible for pulling thread from the spool through the machine. It plays a key role in maintaining consistent thread tension, ensuring even stitch formation and preventing fabric puckering. During the threading process, the thread is hooked into the take-up lever, which works in conjunction with the bobbin case and tension dial to regulate thread flow. Proper adjustment of the take-up lever is essential for balanced stitching. If the tension is too loose or tight, it can lead to stitching issues. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the take-up lever ensure smooth sewing operations and optimal thread utilization, making it an indispensable component for achieving professional results.
2.5 Thread Guide: Directing Thread Flow
The thread guide is a crucial component responsible for directing the thread from the spool through the machine. It ensures the thread flows smoothly and consistently, preventing tangles and knots. Properly threading the machine through the guide is essential for maintaining even tension and stitch quality. The thread guide works in conjunction with the take-up lever, bobbin case, and tension dial to regulate thread flow. If the thread is not guided correctly, it can lead to uneven stitching or machine jamming. Regular inspection and cleaning of the thread guide are necessary to ensure optimal performance and extend the machine’s lifespan. Accurate thread guidance is vital for producing high-quality stitches and achieving professional sewing results.
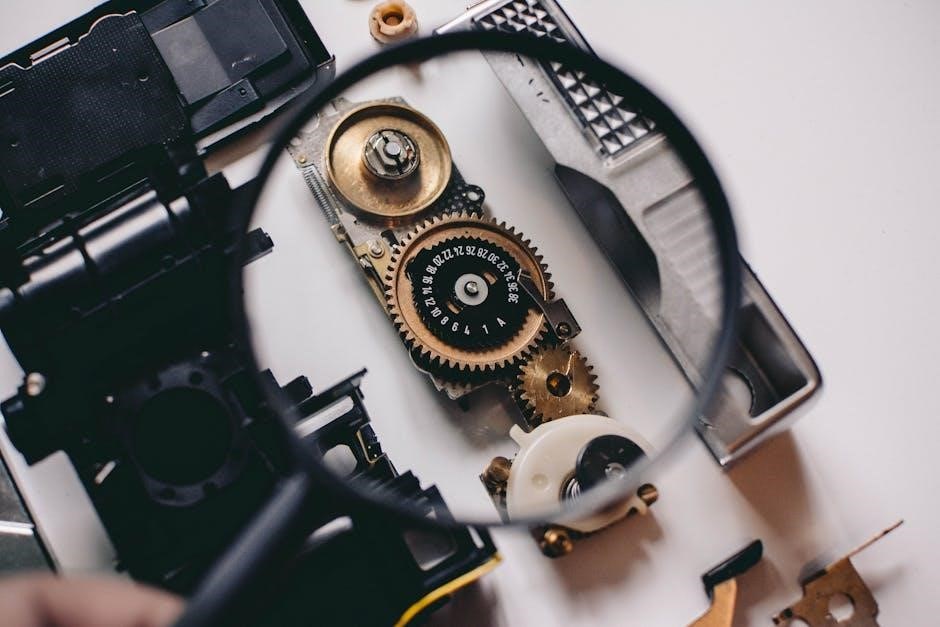
Key Functional Parts of a Sewing Machine
Essential components like the tension dial, presser foot, and feed dog ensure precise fabric control and stitch formation. These parts work harmoniously to deliver smooth sewing operations.
3.1 Tension Dial: Adjusting Thread Tension
The tension dial is a critical component that regulates the balance of thread tension in a sewing machine. Proper adjustment ensures even stitch formation and prevents fabric puckering or loose threading. Located on the front or top of the machine, it allows users to tighten or loosen the thread by rotating it clockwise or counterclockwise. Correct tension is essential for consistent stitching, especially when working with different fabric types or thicknesses. Improper tension can lead to broken threads or uneven seams, making the tension dial a vital tool for achieving professional-looking results in various sewing projects.
3.2 Presser Foot: Fabric Handling and Control
The presser foot is a vital component that holds fabric firmly in place during sewing, ensuring stable movement and even stitch formation. Typically attached to the machine’s shuttle hook, it comes into direct contact with the fabric to prevent slippage. Various types, such as the all-purpose foot and zigzag foot, cater to different sewing tasks, enhancing control over fabric handling. Proper use of the presser foot is essential for maintaining consistent tension and preventing fabric bunching, which can lead to uneven stitching. Its ability to grip and guide the fabric smoothly makes it indispensable for achieving professional-quality results in a wide range of sewing projects.
3.3 Feed Dog: Fabric Movement Mechanism
The feed dog is a metal component located under the presser foot, featuring teeth that grip and move fabric steadily through the machine. Its primary function is to regulate fabric movement, ensuring even stitching and preventing slippage. The feed dog operates in a forward and backward motion, synchronized with the needle’s up-and-down movement. This synchronization is crucial for maintaining consistent stitch length and alignment. Properly adjusted feed dogs are essential for smooth fabric flow, preventing bunching or dragging. They are particularly important for straight-line sewing, where precise control over fabric movement is necessary. Adjusting the feed dog’s height or timing can optimize performance for various fabrics and sewing tasks, ensuring professional-quality results.
3.4 Needle: Stitch Formation and Thread Loop

The needle is a fundamental component of a sewing machine, responsible for stitch formation and creating thread loops. It moves up and down, piercing the fabric to form loops on both the top and bottom layers. The needle’s alignment and timing with other parts, like the bobbin hook or rotary hook, are critical for proper stitch formation. Different needle types and sizes are available for various fabrics and threads, ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and replacing the needle, is essential to prevent damage and ensure smooth operation. The needle’s precise movement and thread loop creation are vital for achieving consistent and professional-quality stitching in every project.

Additional Components and Accessories
Additional components like the bobbin winder, stitch selector, and power switch enhance functionality. Accessories such as extra needles, presser feet, and thread cutters expand sewing capabilities and convenience.
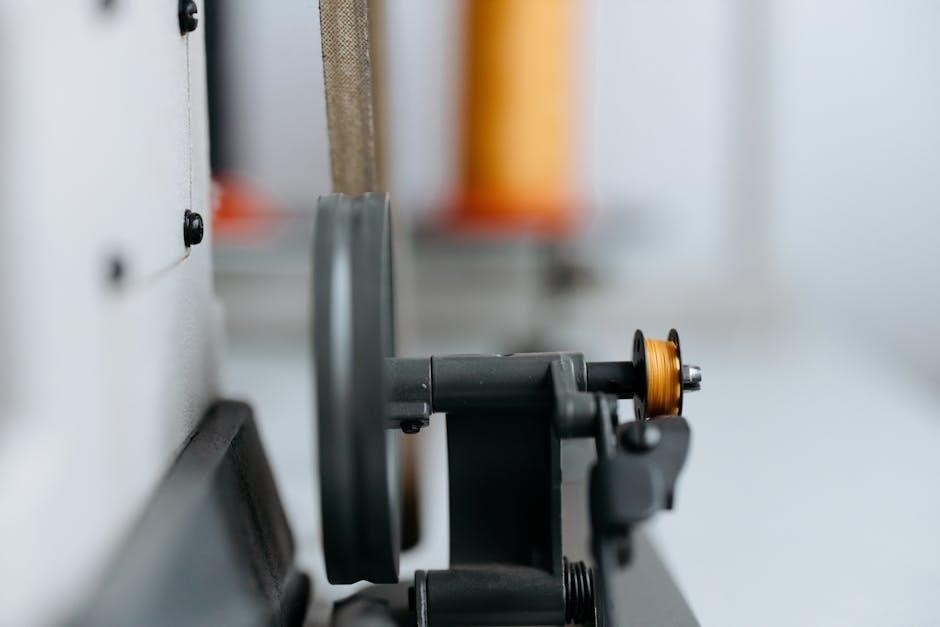
4.1 Bobbin Winder: Winding Thread Efficiently
The bobbin winder is a crucial accessory for efficiently winding thread onto the bobbin. Located on the top or side of the machine, it holds the spool of thread in place. By engaging the winder, the thread is smoothly and evenly wrapped around the bobbin, ensuring consistent tension. This feature saves time by allowing users to prepare multiple bobbins in advance, reducing interruptions during sewing projects. Proper use of the bobbin winder is essential for maintaining the quality of stitches and preventing thread tangles or breakage. Regularly checking the bobbin winder’s alignment and cleanliness ensures optimal performance and longevity of the sewing machine.
4.2 Stitch Selector: Choosing Stitch Patterns
The stitch selector is a key feature that allows users to choose from various stitch patterns, enhancing creativity and versatility in sewing projects. Typically located on the machine’s front or top, it enables the selection of straight stitches, zigzag, or decorative patterns. Modern machines may include a digital display for easy navigation. Proper use of the stitch selector ensures the correct stitch type is applied, matching the fabric and sewing task. Understanding its operation is vital for achieving professional results and exploring diverse sewing techniques. Regularly reviewing the machine’s manual helps master the stitch selector’s functionality, unlocking its full potential for both practical and creative sewing endeavors.
4.3 Power Switch: Operating the Machine
The power switch is a fundamental control element of the sewing machine, enabling users to turn the machine on and off. Typically located on the right side, it provides a straightforward way to manage power supply. The power switch ensures safe and efficient operation, allowing users to start and stop sewing effortlessly. It is essential to familiarize yourself with its placement and function, as it is the primary means of controlling the machine. Proper use of the power switch helps maintain the machine’s longevity and ensures a smooth sewing experience. Always refer to the manual for specific guidance on operating the power switch effectively.
Understanding sewing machine parts is crucial for effective operation and troubleshooting. Proper maintenance and usage ensure longevity and enhance sewing skills. Key components work together harmoniously.
5.1 Summary of Sewing Machine Parts and Functions
A sewing machine consists of essential components like the spool pin, bobbin, take-up lever, and presser foot, each serving specific roles in stitch formation and fabric control. The spool pin holds the thread, while the bobbin manages the underside of stitches. The take-up lever adjusts thread tension, and the presser foot keeps fabric stable. Understanding these parts is vital for troubleshooting and maintaining the machine. Proper threading, bobbin winding, and tension adjustment ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance, such as oiling and cleaning, extends the machine’s lifespan. By mastering these elements, users can optimize their sewing experience and achieve professional results. This knowledge empowers sewers to handle various projects with confidence;
5.2 Importance of Proper Maintenance and Usage
Proper maintenance and usage of a sewing machine are crucial for its performance and longevity. Regular oiling of moving parts, such as the needle bar and hook, prevents friction and ensures smooth operation. Cleaning lint and debris from the bobbin case and feed dog is essential to maintain consistent stitch quality. Using the correct thread type and ensuring proper threading and tension settings prevents thread breakage and uneven stitching. Additionally, regular servicing by a professional can address hidden issues before they escalate. Proper usage involves following the manufacturer’s guidelines for fabric types and stitch selection. By adhering to these practices, users can extend the machine’s life, reduce repair costs, and achieve consistent, professional results in their sewing projects.